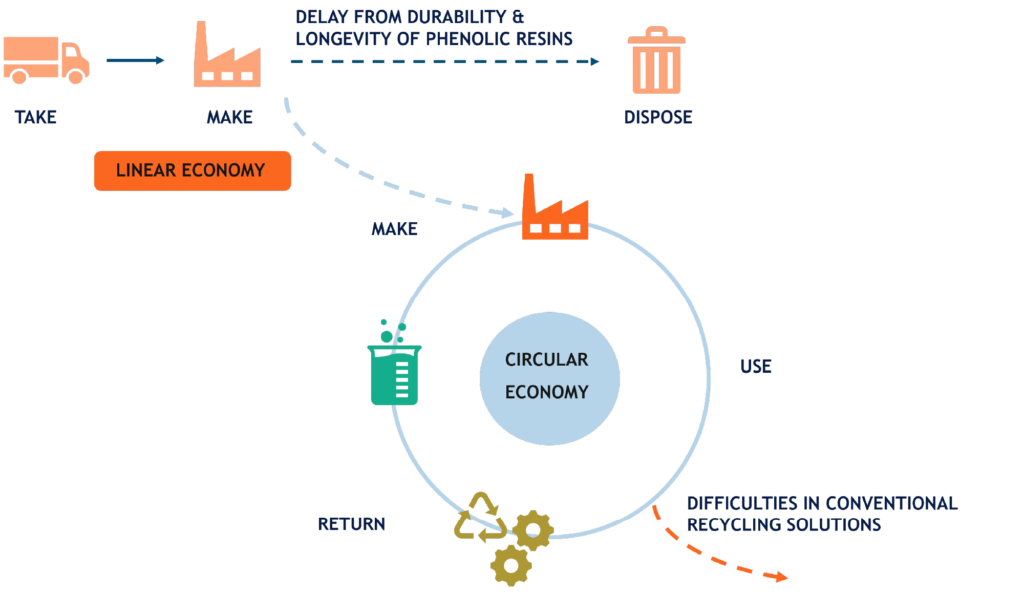
The long-term durability of phenolic resins (up to 60 years in the built environment) enhances the sustainability of the products making recycling questions appear only at the end of a usually long service life. Because phenolic resins are composed of a thermoset, three-dimensional network, they are difficult to breakdown chemically, melted or recast. It is therefore that the very properties that make phenolic resins desirable materials in high-performance appliations also limit their options for recycling.
RECYCLING EXAMPLES

RECYCLING METHODS
Methods are in development to recycle phenolic resins:
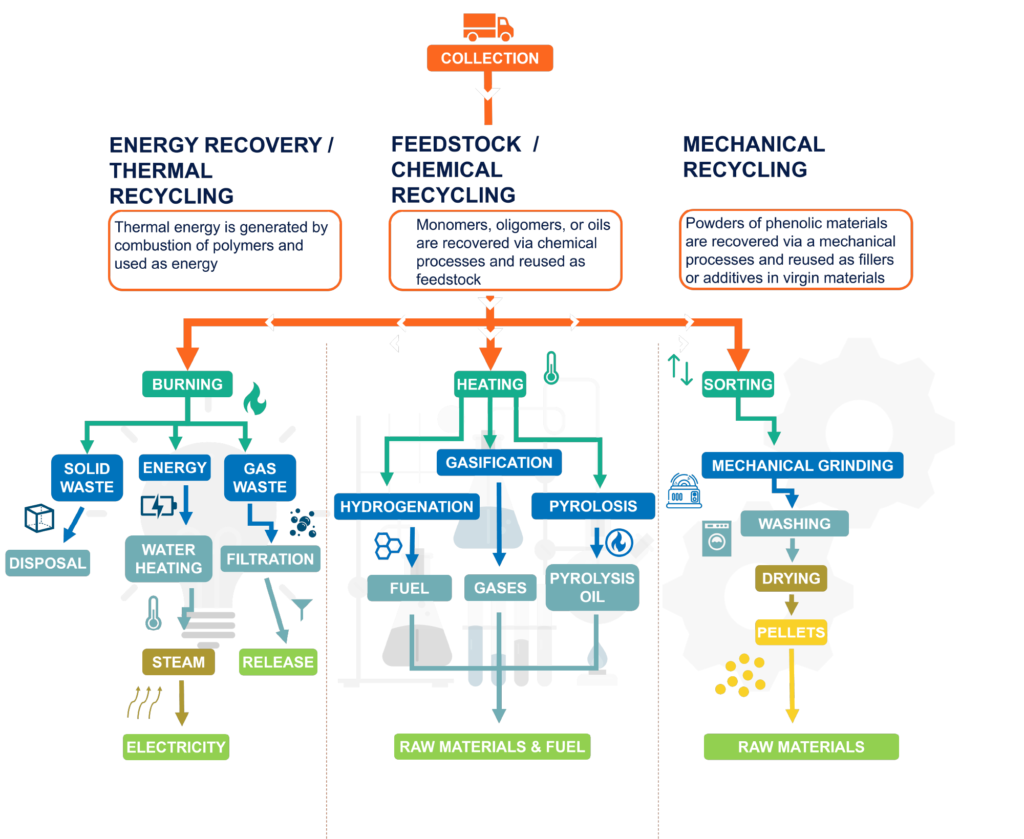
MECHANICAL RECYCLING
- High production efficiency
- Reduce secondary pollution
- Resin performance not comparable to original
- Reuse only as fillers
FEEDSTOCK / CHEMICAL RECYCLING
- Satisfies a wider application area
- Suitable for recycling larger amounts of material
- Technical issues with chemical process
- Requires construction of chemical plant
Although feedstock recycling appears to be particularly promising, not enough progress has been made in this regard.
Aware of the challenges posed by the recycling of phenolic resins, EPRA members are supportive of novel recycling options to contribute to the EU’s circular economy objectives.
